---恢复内容开始---
一、动手动脑:多层的异常捕获-1
阅读以下代码(CatchWho.java),写出程序运行结果:
ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException/内层try-catch
发生ArithmeticException
1、源码:
public class CatchWho { public static void main(String[] args) { try { try { throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(); } catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) { System.out.println( "ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException" + "/内层try-catch"); } throw new ArithmeticException(); } catch(ArithmeticException e) { System.out.println("发生ArithmeticException"); } catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) { System.out.println( "ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException" + "/外层try-catch"); } } } 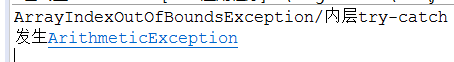
动手动脑:多层的异常捕获-2
写出CatchWho2.java程序运行的结果
ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException/外层try-catch
1、源代码
public class CatchWho2 { public static void main(String[] args) { try { try { throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(); } catch(ArithmeticException e) { System.out.println( "ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException" + "/内层try-catch"); } throw new ArithmeticException(); } catch(ArithmeticException e) { System.out.println("发生ArithmeticException"); } catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) { System.out.println( "ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException" + "/外层try-catch"); } } }
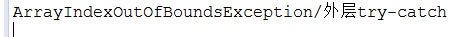
二、当有多个嵌套的try…catch…finally时,要特别注意finally的执行时机。
EmbedFinally.java示例
代码:
public class EmbededFinally { public static void main(String args[]) { int result; try { System.out.println("in Level 1"); try { System.out.println("in Level 2"); // result=100/0; //Level 2 try { System.out.println("in Level 3"); result=100/0; //Level 3 } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("Level 3:" + e.getClass().toString()); } finally { System.out.println("In Level 3 finally"); } // result=100/0; //Level 2 } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("Level 2:" + e.getClass().toString()); } finally { System.out.println("In Level 2 finally"); } // result = 100 / 0; //level 1 } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("Level 1:" + e.getClass().toString()); } finally { System.out.println("In Level 1 finally"); } }} 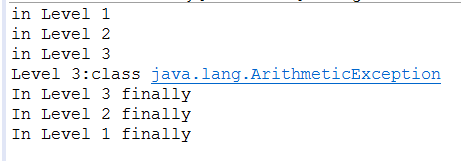
特别注意:
当有多层嵌套的finally时,异常在不同的层次抛出 ,在不同的位置抛出,可能会导致不同的finally语句块执行顺序。
三、辨析:finally语句块一定会执行吗?
SystemExitAndFinally.java示例
代码:
public class SystemExitAndFinally { public static void main(String[] args) { try{ System.out.println("in main"); throw new Exception("Exception is thrown in main"); //System.exit(0) } catch(Exception e) { System.out.println(e.getMessage()); //System.exit(0); } finally { System.out.println("in finally"); } }} 
总结:无论catch()语句有没有运行finally()语句都会执行,但如果层序的前面有Syatem.exit(1);finally()则不能执行。
四、编写一个程序,此程序在运行时要求用户输入一个 整数,代表某门课的考试成绩,程序接着给出“不及格”、“及格”、“中”、“良”、“优”的结论。
要求程序必须具备足够的健壮性,不管用户输入什 么样的内容,都不会崩溃。
1、源代码
import java.util.Scanner;public class Grade{ public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("请输入学生成绩:"); String sub=in.next(); for(int i=0;i =57||sub.charAt(i)<=48)try { throw new Exception(sub);} catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("输入错误,请输入学生成绩:"); sub=in.next(); } } if(Integer.parseInt(sub)>=90&&Integer.parseInt(sub)<=100) {System.out.println("该学生成绩为:"+sub+"\n优秀呢!");} if(Integer.parseInt(sub)>=80&&Integer.parseInt(sub)<90) {System.out.println("该学生成绩为:"+sub+"\n良等!");} if(Integer.parseInt(sub)>=70&&Integer.parseInt(sub)<80) {System.out.println("该学生成绩为:"+sub+"\n中等!");} if(Integer.parseInt(sub)>=60&&Integer.parseInt(sub)<70) {System.out.println("该学生成绩为:"+sub+"\n及格喽!");} if(Integer.parseInt(sub)>=0&&Integer.parseInt(sub)<60) {System.out.println("该学生成绩为:"+sub+"\n你不及格哎!");} }} 
---恢复内容结束---